Weizmann Institute Introduces P53 Target Anti-Cancer Drugs
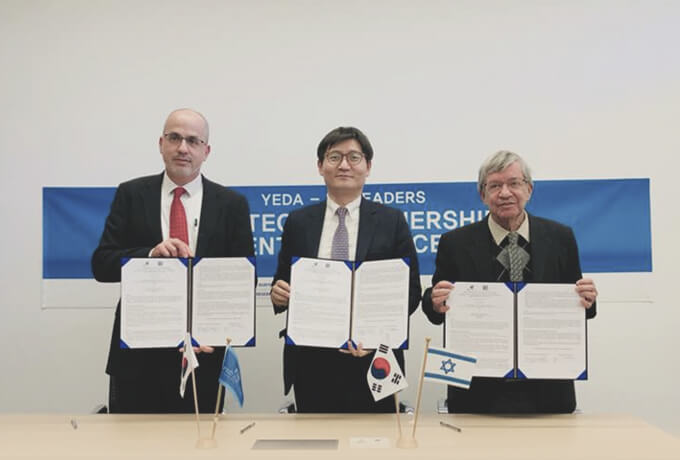
Promoting the Establishment of an R&D Joint Venture with Israeli YEDA
Weizmann Institute
Introduces P53 Target
Anti-Cancer Drugs

01
Promoting
the Establishment
of an R&D Joint
Venture with Israeli
YEDA

02
Inactivation of p53 in Tumors
Confers a Strong Selective Advantage
in the Carcinogenic Process
Eliminating p53 function may be a prerequisite
for tumor survival 1-3
Preclinical work has shown that the absence of p53
function is a continuous resquirement for the maintenance
of established tumors
Loss of functioning p53 promotes the
oncogenic phenotype 4
Cellular insults trigger phosphorylation of the
N-terminal domain of p53 leading to conformational
changes 5.6
Prevention of p53 degradation, prolonged molecular half-
life, accumulation of p53 at high levels
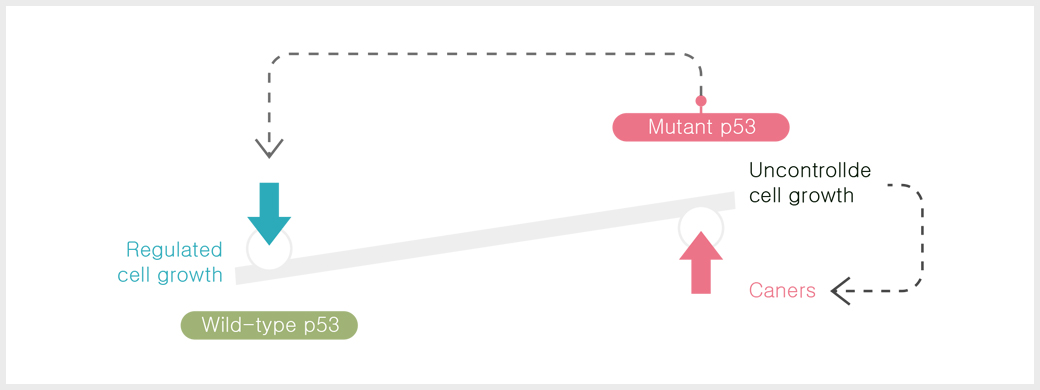
Cells without normal fuctioning p53 fail to recognize
and address cellular stressors/abnormalities, allowing
uncontrolled replication of affected cells 4
When p53 is functioning properly, oncogenic mutations
are not propagated, as DNA repair activities are intact
and cell cycling is tightly controlled 6
2. Martins CP, Brown-Swigart L, Evan Gl. Cell. 2006;127:1323-1334.
3. Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, et al. Nature. 2001/doi:10:10.1038/nature05529.
4.Toledo F, Wahl GM. Nature Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:909-923
5. Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Nature. 2000;408:307-310.
6. Nag S, Qin J, Srivenugopal KS, et al. J Biomed Res, 2013;27:254-271

03
p53 is the Most Frequently Altered
Gene in Human Cancer
Somatic mutations in p53 have been seen in
several human tumors types-p53 multations or
deletions are observed in apporoximately 50%
of all solid tumors
Missense multations in p53 are frequent, and
can resu in gain of function changes that
enhance metastatic potential and invasiveness
In many tumor types, p53 mutations have
been associated with a poorer prognosis
with diminished overall survival and more
aggressive tumor behavior
p53 is not mutated in up to 50% of solid
tumors and is generally not mutated in
hematologic malignancies
In these tumors, wild-type p53(p53wt) is most likely
inactivated - inacyivation of p53 plays a critical role in
development and progression of the cancer5
2. Eischen CM, Lozano G. Human Mutation. 2014; 35:728-737.
3. Ventuar A, Kirs DG, McLaughlin ME, et al. Nature. 2007; 445:661-665
4. VuBT, Vassilev LT. Curr Topics Micrbio Immunol. 2011;348:151-172.
5. Pal S, Bhattacharjee A, Ali A, et al, J Inflammation. 2014;11023
Why p53 reactivation?
Tackling fundamental problems underlying cell proliferation and oncogenesis will provide an effective solution to develop an innovative, life-saving cancer therapy.
- * Arrested cell proliferation
- * Death of cancer cells
- * Sensitization of refractory cancers